前言
在开发过程中我们看到的程序入口都是 main 函数,所以认为程序都是从 main 函数开始执行的。其实在程序执行 main 函数之前已经执行了 +load 和 constructor 构造函数。今天我们就来看看在 main 函数执行之前都发生了什么。
什么是 dyld ?
程序运行依赖于很多动态库,动态库也是一个静态文件,格式和 iOS、MacOS、WatchOS 的可执行文件格式是一样的,都是 Mach-O 文件。他本身是不可以直接运行的,需要通过一个动态库加载器将其加载到内存空间,那么这个动态链接加载器就是 dyld 了。
dyld 源码分析
dyld 在手机中的路径是 /usr/lib/dyld,这是源码下载地址 dyld源码 。
代码从 dyldStartup.s 文件开始执行,下面我们看看用汇编实现的 __dyld_start 方法。
1 | #if __arm64__ |
我们看到在 __dyld_start 中调用了 dyldbootstrap::start 。下面我们就看看 dyldbootstrap::start 做了什么:
1 | uintptr_t start(const struct macho_header* appsMachHeader, int argc, const char* argv[], |
上面看到了调用 dyld::_main 函数,其实在该函数中便完成了整个动态库加载的一系列过程,接下来我们仔细看看中间都做了什么:
1 | uintptr_t |
在 dyld::_main 函数的最后,找到主程序 main 函数的地址,此时 dyld 加载动态库的流程就结束了,进入到了我们熟悉的 main 函数。
简单流程
整个动态库加载的流程主要包括以下个步骤:
1.设置上下文信息,配置进程是否受限
首先调用 setContext 设置上下文信息,然后调用 configureProcessRestrictions 设置进程是否受限。只要设置了 uid 和 gid 就会变成受限模式。受限模式其实就是忽略 DYLD 环境变量。
值得一提的是在 iOS10.3.2 及以上版本中,设置 Other Linker Flags 为 -Wl,-sectcreate,__RESTRICT,__restrict,/dev/null 也不能阻止 DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES 的注入。
2.配置环境变量,获取当前运行架构
调用 checkEnvironmentVariables 根本环境变量设置相应的值,但是如果 sEnvMode 为 envNone (受限模式),就直接跳过,否则调用 processDyldEnvironmentVariable 处理并设置环境变量。
调用 getHostInfo 获取当前运行的架构信息。
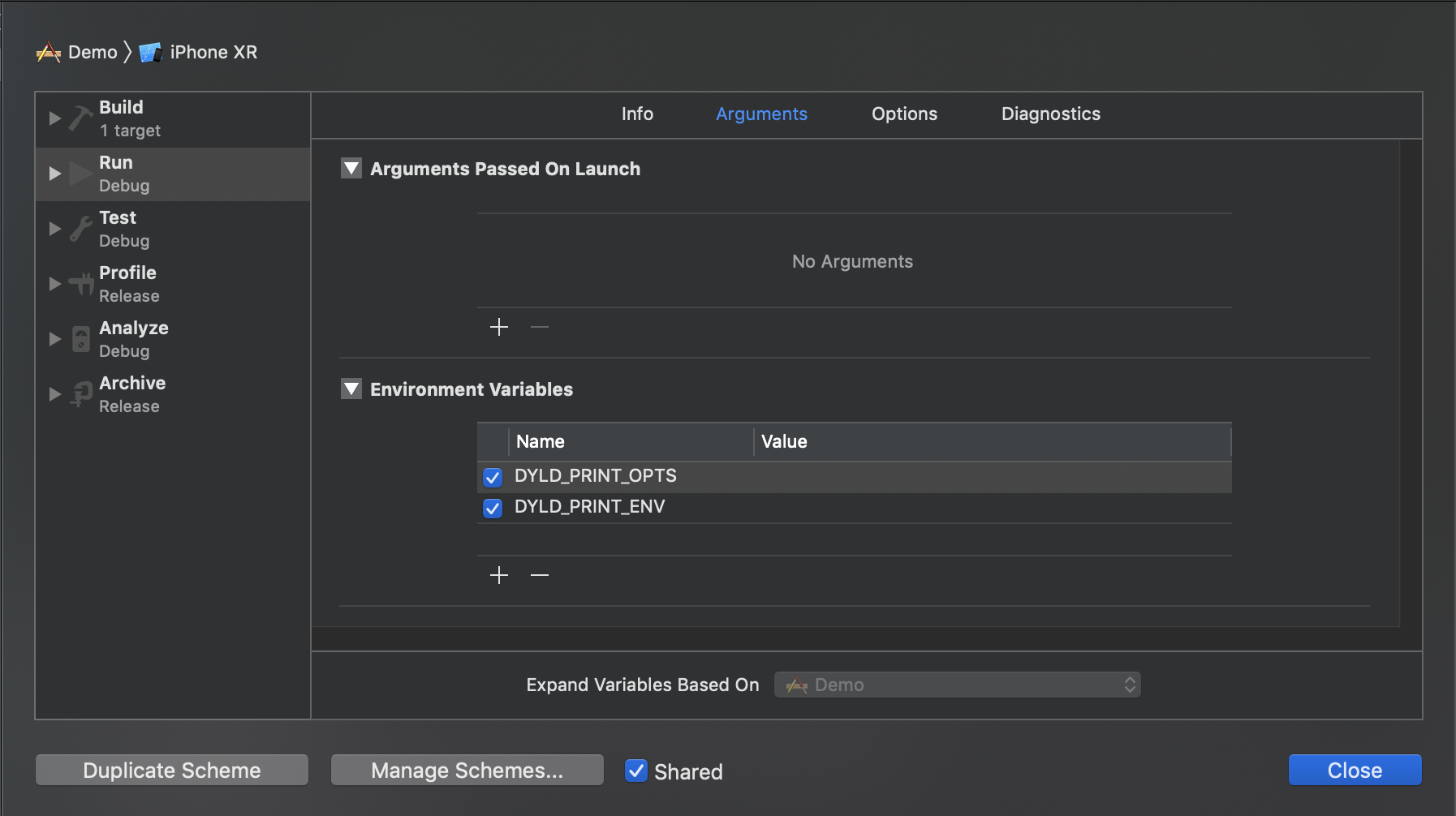
在开发中,我们可以点击 Edit Scheme 在环境变量添加 DYDLD_PRINT_OPTS 和 DYLD_PRINT_ENV ,就能打印当前参数和环境变量。
1 | // 如果设置 DYDLD_PRINT_OPTS 环境变量,则打印 |
3.加载可执行文件,生成一个 ImageLoader 实例对象
调用 instantiateFromLoadedImage 函数来实例化一个 ImageLoader 对象。
作为主程序初始化的 imageLoader 用于后续的链接等过程,主程序作为 dyld 的第一个被 addimage 的镜像,所以我们总是能够通过_dyld_get_image_header(0) 或者 _dyld_get_image_name(0) 等,索引到第一个 image 镜像为主程序的相关信息。
4.检查共享缓存是否映射到了共享区域
5.加载所有插入的库
遍历 DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES 环境变量,然后调用 loadInsertDylib 加载。
6.链接主程序
调用 link 链接主程序。
7.链接所有插入的库,执行符号替换
对 sAllImage(除第一项主程序)中的库调用 Link 函数进行链接,然后调用 register Interposing 注册符号替换。
8.执行初始化方法
initializeMainExecutable() 执行初始化方法,+load 和 constructor 构造方法就是在这里执行的。
9.寻找主程序入口
调用 getThreadPC() 读取 LC_MAIN 入口,如果找不到就读取 LC_UNIXTHREAD ,然后跳转到程序入口处执行,这样就来到了 main 函数。
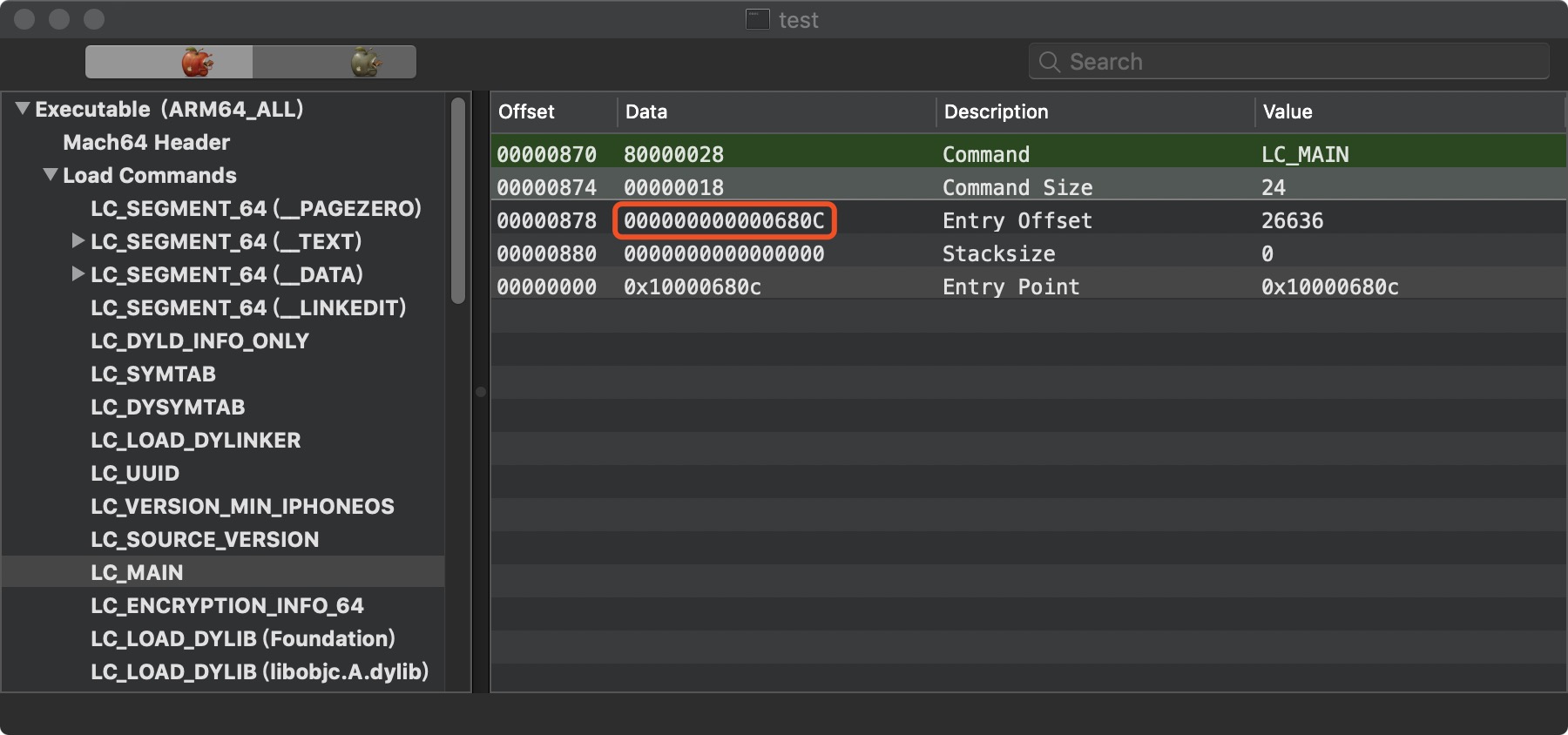
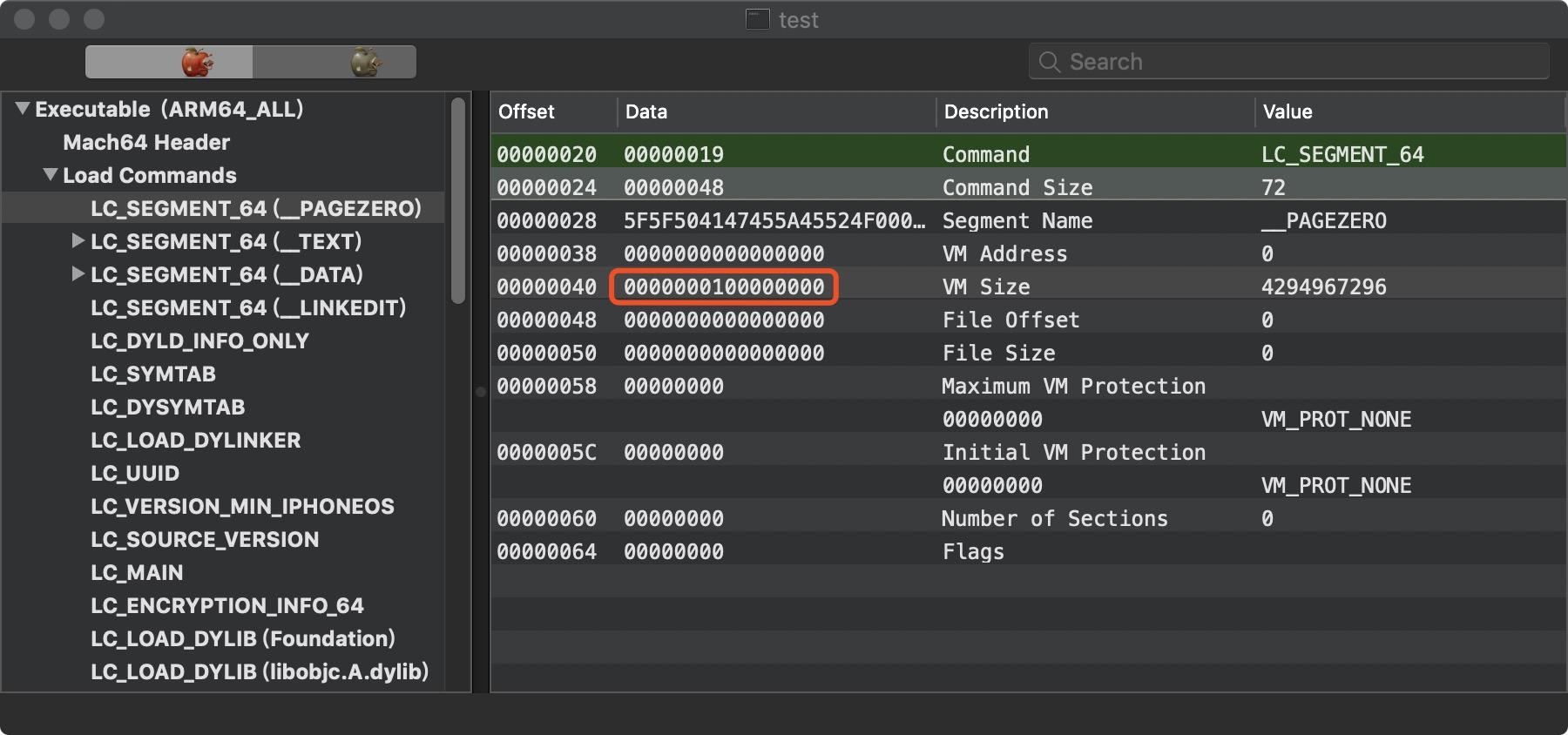
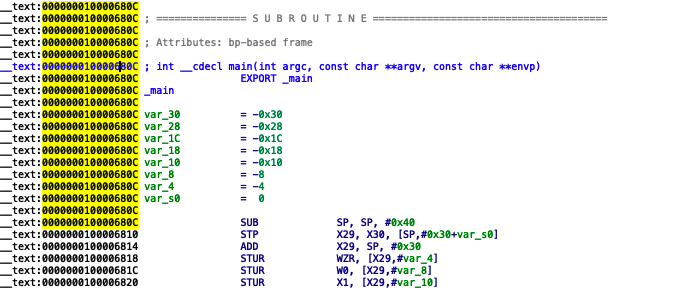
LC_MAIN 加上 Load Commands 的 VM Size 就是我们程序 mian 函数的地址。
写在后面
我们现在搞清楚了 dyld 是如何加载的,以及从 __dyld_start 到 mina 之间都做了什么,那么 dyld 又是被谁调用的呢?下次让我们继续分析。